Key Points In the short run, there are both fixed and variable costs. In the long run, there are no fixed costs. Efficient long run costs are sustained when the combination of outputs that a firm produces results in the desired quantity of the goods at the lowest possible cost. Variable costs change with the output.
Understanding Firm Short Run Cost Curves – YouTube
Analyze short-run costs in terms of total cost, fixed cost, variable cost, marginal cost, and average cost Calculate average profit Evaluate patterns of costs to determine potential profit We’ve explained that a firm’s total costs depend on the quantities of inputs the firm uses to produce its output and the cost of those inputs to the firm.

Source Image: navi.com
Download Image
Figure 8.9 Relationship Between Short-Run and Long-Run Average Total Costs. The LRAC curve is found by taking the lowest average total cost curve at each level of output. Here, average total cost curves for quantities of capital of 20, 30, 40, and 50 units are shown for the Lifetime Disc Co. At a production level of 10,000 CDs per week
Source Image: economicsmicro.blogspot.com
Download Image
Long Run Cost Curves: Total, Average and Marginal Costs with Examples Equation 8.8. [latex]AVC + AFC = ATC [/latex] the distance between the curves keeps getting smaller and smaller as the firm spreads its overhead costs over more and more output. Marginal Cost, Average Fixed Cost, Average Variable Cost, and Average Total Cost in the Short Run.

Source Image: courses.lumenlearning.com
Download Image
Short Run Cost And Long Run Cost
Equation 8.8. [latex]AVC + AFC = ATC [/latex] the distance between the curves keeps getting smaller and smaller as the firm spreads its overhead costs over more and more output. Marginal Cost, Average Fixed Cost, Average Variable Cost, and Average Total Cost in the Short Run. In summary, the short run and the long run in terms of cost can be summarized as follows: Short run: Fixed costs are already paid and are unrecoverable (i.e. “sunk”). Long run: Fixed costs have yet to be decided on and paid, and thus are not truly “fixed.” The two definitions of the short run and the long run are really just two ways of saying
Reading: Short Run and Long Run Average Total Costs | Microeconomics
Short Run vs. Long Run Costs Our analysis of production and cost begins with a period economists call the short run. The short run in this microeconomic context is a planning period over which the managers of a firm must consider one or more of their factors of production as fixed in quantity. Economics Blog: How do you explain Economies of scale
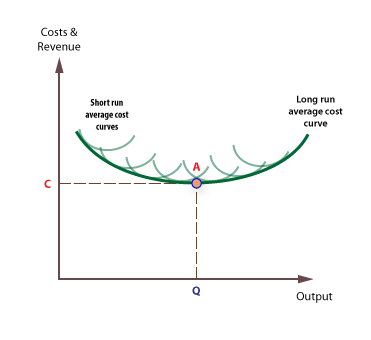
Source Image: economicsgceopastanswers.blogspot.com
Download Image
Short-Run Costs and Long-Run Costs | bartleby Short Run vs. Long Run Costs Our analysis of production and cost begins with a period economists call the short run. The short run in this microeconomic context is a planning period over which the managers of a firm must consider one or more of their factors of production as fixed in quantity.
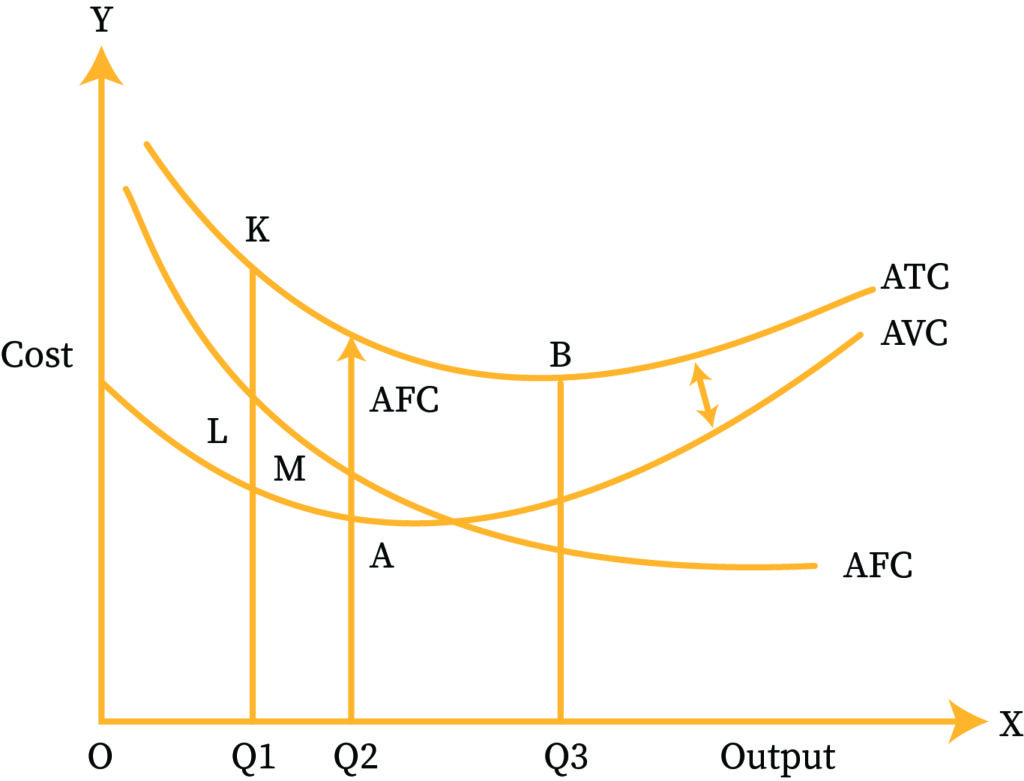
Source Image: bartleby.com
Download Image
Understanding Firm Short Run Cost Curves – YouTube Key Points In the short run, there are both fixed and variable costs. In the long run, there are no fixed costs. Efficient long run costs are sustained when the combination of outputs that a firm produces results in the desired quantity of the goods at the lowest possible cost. Variable costs change with the output.

Source Image: youtube.com
Download Image
Long Run Cost Curves: Total, Average and Marginal Costs with Examples Figure 8.9 Relationship Between Short-Run and Long-Run Average Total Costs. The LRAC curve is found by taking the lowest average total cost curve at each level of output. Here, average total cost curves for quantities of capital of 20, 30, 40, and 50 units are shown for the Lifetime Disc Co. At a production level of 10,000 CDs per week

Source Image: toppr.com
Download Image
Diagrams of Cost Curves – Economics Help ShortRun Total Cost: ADVERTISEMENTS: A typical short-run total cost curve (STC) is shown in Fig. 14.3. This curve indicates the firm’s total cost of production for each level of output when the usage of one or more of the firm’s resources remains fixed.
Source Image: economicshelp.org
Download Image
Short run cost, Long run Cost Equation 8.8. [latex]AVC + AFC = ATC [/latex] the distance between the curves keeps getting smaller and smaller as the firm spreads its overhead costs over more and more output. Marginal Cost, Average Fixed Cost, Average Variable Cost, and Average Total Cost in the Short Run.

Source Image: theintactone.com
Download Image
Long-Run versus Short-Run Cost Curves – HKT Consultant In summary, the short run and the long run in terms of cost can be summarized as follows: Short run: Fixed costs are already paid and are unrecoverable (i.e. “sunk”). Long run: Fixed costs have yet to be decided on and paid, and thus are not truly “fixed.” The two definitions of the short run and the long run are really just two ways of saying
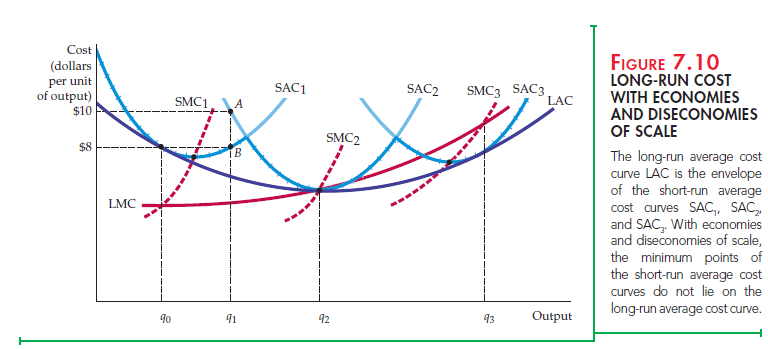
Source Image: phantran.net
Download Image
Short-Run Costs and Long-Run Costs | bartleby
Long-Run versus Short-Run Cost Curves – HKT Consultant Analyze short-run costs in terms of total cost, fixed cost, variable cost, marginal cost, and average cost Calculate average profit Evaluate patterns of costs to determine potential profit We’ve explained that a firm’s total costs depend on the quantities of inputs the firm uses to produce its output and the cost of those inputs to the firm.
Long Run Cost Curves: Total, Average and Marginal Costs with Examples Short run cost, Long run Cost ShortRun Total Cost: ADVERTISEMENTS: A typical short-run total cost curve (STC) is shown in Fig. 14.3. This curve indicates the firm’s total cost of production for each level of output when the usage of one or more of the firm’s resources remains fixed.